Virtual Pebble
On this page... (hide)
1. Background and Motivations
Vibrational feedback is readily available and widely used in the community for providing haptic feedback. However, it is very difficult to distinguish multiple vibrational feedback when they occur simultaneously, and even more so difficult when the task becomes more involved.
We found from both the research and our direct experience that as we increase the number of vibrational feedback actuations, the user become more overwhelmed. In this project, we seek to find a way to provide a haptic feedback that is easily distinguishable from the traditional vibrotactile feedback while still providing useful information to the users.
2. Virtual Pebble
Virtual pebble is a wearable haptic device that simulate having a small pebble in a shoe on command. It gives a sensation that is not so painful, but definitely annoying. This motivates the users to correct their motions (in the context of movement training). Once corrected, the pebble disappears.
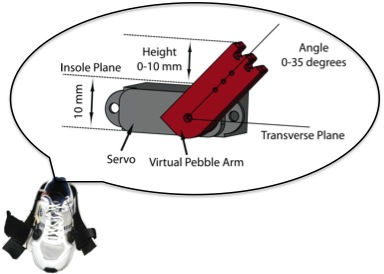
Current version of virtual pebble is a small and thin profile servo embedded in the insole near the heel location
3. Experiments
3.1 Absolute Threshold Perception
With varying amplitudes of haptic feedback, an absolute threshold value was identified by performing a one-up-three-down method.
3.2 Feedback Identification
Users were asked to identify different combinations of haptic feedback in randomized order while standing, walking, and jogging.
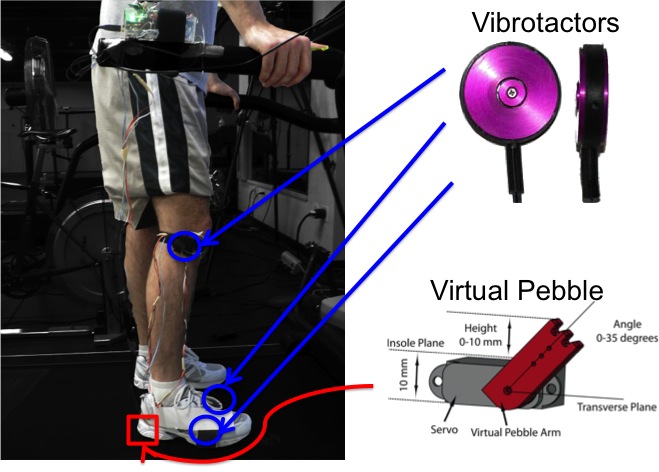
Locations and types of haptic feedback during experiment
4. Results
4.1 Absolute Threshold Perception
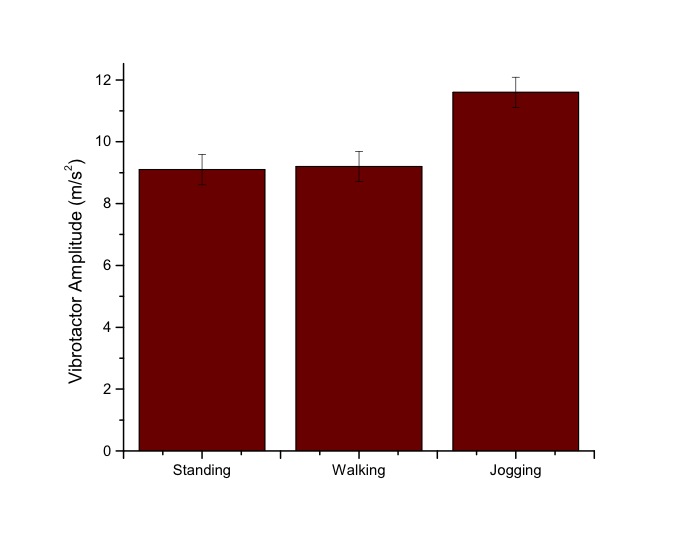
Thresholds for vibrational feedback increases as the speed of movement increases. This may be due to the higher frequency noise introduced by the movement.
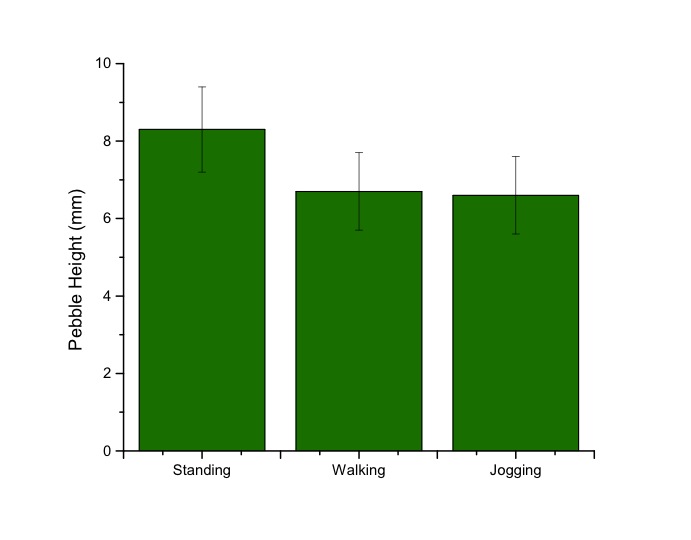
Thresholds for virtual pebble decreases as the speed of movement increases. This may be due to the fact that pebble primarily stimulates slowly-adapting mechanoreceptors
4.2 Feedback Identification
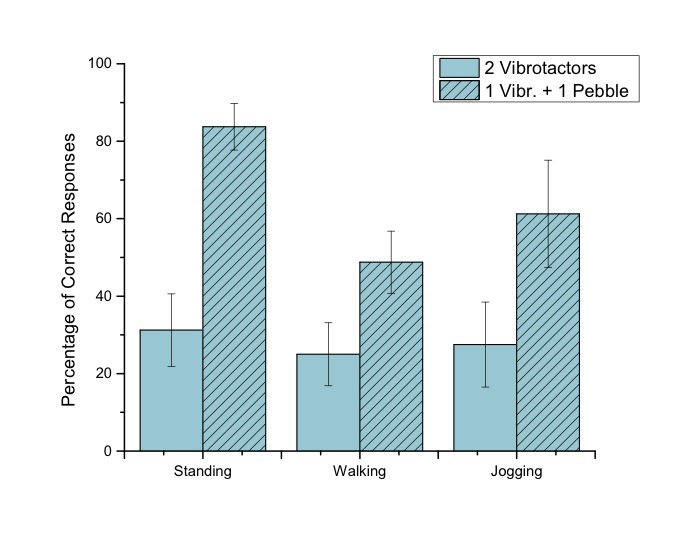
For a combination of feedback on foot, a combination with the pebble has higher perception accuracy in all three conditions
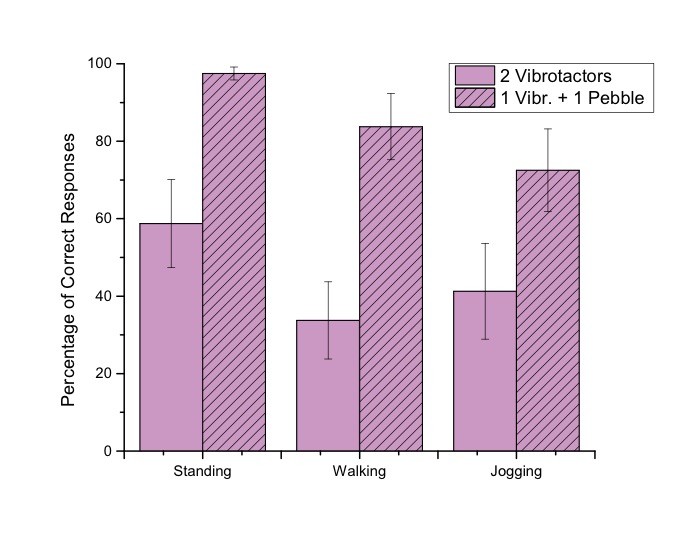
For a combination of feedback on foot and knee, a combination with the pebble has higher perception accuracy in all three conditions
5. What's New?
- August 2, 2011: Presenting "Virtual Pebble: a Haptic State Display for Pedestrians" at RO-MAN 2011 Conference in Atlanta, Georgia

